Robotic device engineered to help stroke survivors recover
10 Jun 2017
A recent study, affiliated with South Korea's Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) has introduced a new robotic tool for assessments of muscle overactivity and movement dysfunction in stroke survivors. Their robotic-assisted rehabilitation therapy, combined with standard rehabilitation, is expected to improve the mobility of patients surviving a stroke.
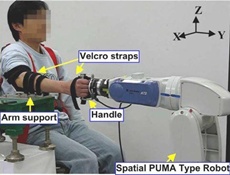 This breakthrough research has been led by Professor Sang Hoon Kang of Mechanical, Aerospace and Nuclear Engineering at UNIST in collaboration with Professor Pyung-Hun Chang of DGIST and Dr Kyungbin Park of Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.
This breakthrough research has been led by Professor Sang Hoon Kang of Mechanical, Aerospace and Nuclear Engineering at UNIST in collaboration with Professor Pyung-Hun Chang of DGIST and Dr Kyungbin Park of Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.
In their study, published in the May issue of the prestigious journal, IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, Professor Kang and his team developed a rehabilitation robotic system that quantitatively measures the 3 degree-of-freedom (DOF) impedance of human forearm and wrist in minutes.
Using their impedance estimation device, entitled the distal internal model based impedance control (dIMBIC)-based method, the team was able to accurately characterise the 3 DOF forearm and wrist impedance, including inertia, damping, and stiffness, for the first time.
Stroke, known as a leading cause of long-term disability, is a sudden loss of brain function, caused by the interruption of blood flow to the brain or the rupture of a blood vessels in the brain. An estimated 150,000 people die from it, each year.
As a consequence of stroke, stroke survivors are often left with muscle overactivity, including spasticity. Spasticity is a muscle control disorder that is characterised by tight or stiff muscles and an inability to control those muscles. It is often manifested by increased stretch reflex activity and mechanical joint resistance.
"The dIMBIC-based method can be used to assist in the quantitative and objective evaluation of neurological disorders, like stroke," says Professor Kang. "Findings from this study will open a new chapter in robot-assisted rehabilitation in the workplace accident rehabilitation hospitals, as well as in nursing homes and assisted living facilities."
The research team expects that, in the long run, the proposed 3 DOF impedance estimation may promote wrist and forearm motor control studies and complement the diagnosis of the alteration in wrist and forearm resistance post-stroke by providing objective impedance values including cross-coupled terms.


















