Engineers 3-D print a 'living tattoo'
07 Dec 2017
MIT engineers have devised a 3-D printing technique that uses a new kind of ink made from genetically programmed living cells.
 | |
| MIT engineers have devised a 3-D printing technique that uses a new kind of ink made from genetically programmed living cells / Image: Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license. |
The cells are engineered to light up in response to a variety of stimuli. When mixed with a slurry of hydrogel and nutrients, the cells can be printed, layer by layer, to form three-dimensional, interactive structures and devices.
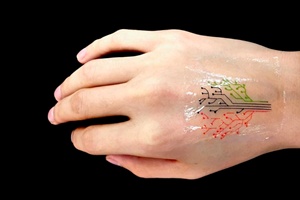
The team has then demonstrated its technique by printing a "living tattoo" - a thin, transparent patch patterned with live bacteria cells in the shape of a tree. Each branch of the tree is lined with cells sensitive to a different chemical or molecular compound. When the patch is adhered to skin that has been exposed to the same compounds, corresponding regions of the tree light up in response.
The researchers, led by Xuanhe Zhao, the Noyce Career Development Professor in MIT's Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Timothy Lu, associate professor of biological engineering and of electrical engineering and computer science, say that their technique can be used to fabricate "active" materials for wearable sensors and interactive displays. Such materials can be patterned with live cells engineered to sense environmental chemicals and pollutants as well as changes in pH and temperature.
What's more, the team developed a model to predict the interactions between cells within a given 3-D-printed structure, under a variety of conditions. The team says researchers can use the model as a guide in designing responsive living materials.
Zhao, Lu, and their colleagues have published their results today in the journal Advanced Materials. The paper's co-authors are graduate students Xinyue Liu, Hyunwoo Yuk, Shaoting Lin, German Alberto Parada, Tzu-Chieh Tang, Eléonore Tham, and postdoc Cesar de la Fuente-Nunez.
A hardy alternative
In recent years, scientists have explored a variety of responsive materials as the basis for 3D-printed inks. For instance, scientists have used inks made from temperature-sensitive polymers to print heat-responsive shape-shifting objects. Others have printed photoactivated structures from polymers that shrink and stretch in response to light.
Zhao's team, working with bioengineers in Lu's lab, realised that live cells might also serve as responsive materials for 3D-printed inks, particularly as they can be genetically engineered to respond to a variety of stimuli.
The researchers are not the first to consider 3-D printing genetically engineered cells; others have attempted to do so using live mammalian cells, but with little success.
"It turns out those cells were dying during the printing process, because mammalian cells are basically lipid bilayer balloons," Yuk says. "They are too weak, and they easily rupture."
Instead, the team identified a hardier cell type in bacteria. Bacterial cells have tough cell walls that are able to survive relatively harsh conditions, such as the forces applied to ink as it is pushed through a printer's nozzle. Furthermore, bacteria, unlike mammalian cells, are compatible with most hydrogels - gel-like materials that are made from a mix of mostly water and a bit of polymer. The group found that hydrogels can provide an aqueous environment that can support living bacteria.
The researchers carried out a screening test to identify the type of hydrogel that would best host bacterial cells. After an extensive search, a hydrogel with pluronic acid was found to be the most compatible material. The hydrogel also exhibited an ideal consistency for 3-D printing.
"This hydrogel has ideal flow characteristics for printing through a nozzle," Zhao says. "It's like squeezing out toothpaste. You need [the ink] to flow out of a nozzle like toothpaste, and it can maintain its shape after it's printed."
From tattoos to living computers
Lu provided the team with bacterial cells engineered to light up in response to a variety of chemical stimuli. The researchers then came up with a recipe for their 3-D ink, using a combination of bacteria, hydrogel, and nutrients to sustain the cells and maintain their functionality.
"We found this new ink formula works very well and can print at a high resolution of about 30 micrometers per feature," Zhao says. "That means each line we print contains only a few cells. We can also print relatively large-scale structures, measuring several centimeters."



















