Cancer drug may cause women to grow new eggs, study suggests
07 Dec 2016
Women treated with a common chemotherapy drug combination have more young eggs in their ovaries afterwards, research has found.
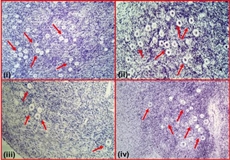 | |
| Follicles in ovarian tissue from (i) a 22-year-old treated with ABVD chemotherapy, (ii) from an untreated 8-year-old; (iii) a healthy 23-year-old; and following OEPA COPDAC chemotherapy treatment (iv) / University of Edinburgh |
A small study indicates that a therapy commonly used to target Hodgkin's lymphoma appears to increase the number of non-growing eggs in women's ovaries.
Researchers say it is too soon to link the outcome to fertility, but believe more research is needed to better understand the findings and their implications.
Scientists from the University of Edinburgh analysed samples of ovary tissue donated by 14 women who had undergone chemotherapy, and from 12 healthy women.
They found that the ovaries from eight of the cancer patients, who had been treated with a drug combination known as ABVD, had a much greater incidence of immature, or non-growing, eggs compared with tissue from women who had received a different chemotherapy, or from healthy women of a similar age.
The ovary tissue was seen to be in healthy condition, appearing similar to tissue from young women's ovaries.
If further research can reveal the mechanism by which treatment with ABVD results in increased production of eggs, this would aid understanding of how women might be able to produce more eggs during their lifetime, which was until recently thought to be impossible.
Researchers had set out to better understand why treatment with ABVD is one of the few cancer drug combinations that does not impact on women's fertility.
Future studies will examine the separate impact of each of the four drugs that combine to make ABVD - known as adriamycin, bleomycin, vinblastine and dacarbazine - to better understand the biological mechanisms involved.
The study, published in Human Reproduction, was supported by the Medical Research Council.
Lead researcher Professor Evelyn Telfer of the University of Edinburgh's School of Biological Sciences, said: "This study involves only a few patients, but its findings were consistent and its outcome may be significant and far-reaching. We need to know more about how this drug combination acts on the ovaries, and the implications of this."


















