New cause of diabetes
18 Feb 2016
A common cause of diabetes is a deficiency of insulin-producing cells in the endocrine tissue of the pancreas. New findings suggest the exocrine tissues of the pancreas instead could make a promising target for stem cell-based diabetes treatment.
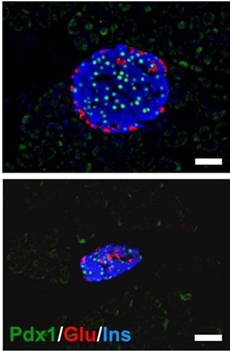 | |
| In normal mice (top), the pancreas forms with normal spatial organization as seen by the distinct patterning of different colored cell types. In Pdx1 mutant mice (bottom), however, the pancreas is much smaller and loses its spatial organization. Scale bars = 50 micro meter. / Credit: Kawaguchi Laboratory, CiRA, Kyoto University |
Diabetes describes a disease where the body is not receiving a sufficient supply of insulin. It commonly inflicts the pancreas, the organ responsible for insulin production. More specifically, it inflicts the cells that produce insulin, which are found in the endocrine tissue of the pancreas. However, new results from the Yoshiya Kawaguchi lab suggest the exocrine tissue, which is responsible for digestion, could have a role in treatment.
"The pancreas is constituted of two tissues that are structurally and functionally distinct, which makes it unique", says Prof. Yoshiya Kawaguchi of the Center for iPS Cell Research and Application, Kyoto University, which is why most researchers attend the endocrine tissue for diabetes.
However, while the exocrine and endocrine tissues operate independently in mature pancreas, they are formed at the same time during pancreas development. Kawaguchi wondered if diseased exocrine tissue could cause deficiencies in the production of endocrine cells. To investigate this possibility, his team constructed mice that depleted the Pdx1 gene, which in the pancreas is exclusively found in exocrine tissue.
The result was underdeveloped pancreas, but in addition, and surprisingly, the mice showed diabetes phenotype, such as low insulin levels, suggesting endocrine development was also affected. However, what caught the researchers' attention was which cells had changed. Endocrine progenitor cells that did not have the mutation in the mutant mice also showed poor survival. These results suggest non-cell autonomous effects, which describes the phenomenon where cells with genetic defects may cause malfunction in neighboring, genetically healthy cells, and could have important implications for diabetes treatment.
"This is an exciting finding", explains Kawaguchi, adding, "It means the exocrine cells secrete something that promotes the differentiation and survival of endocrine cells during development". This substance, Kawaguchi hopes, could lead to promising treatments for diabetes.


















