India among top 10 spam sources in Q1 2014
12 May 2014
In the first quarter of 2014 spammers started imitating messages from mobile applications.
They especially like the popular mobile messengers WhatsApp, Viber and Google Hangouts: notifications purportedly sent from these applications were used to
spread both malware and harmless adverts.
The rising popularity of mobile devices means that phishing attacks targeting Apple IDs are becoming more frequent.
Many gadget owners are used both to synchronisation of their contacts and to the
fact that messages from mobile applications can arrive via email, so few would be
suspicious of the fact that WhatsApp is not directly linked to an email service.
This lack of caution could prove costly, since the attached archive contained the notorious Backdoor.Win32.Androm.bjkd, whose main function is to steal personal data from users.
Altaf Halde, managing director, Kaspersky Lab South Asia, said, "The bad
guys constantly develop new ways to attack your smart phones and computers
in order to steal personal information. Most popular malicious programs are now multifunctional, they can steal data from the victims computer, make the computer part of a botnet or download and install other malicious programs without the user's knowledge.
"This is why it is extremely critical to update your operating system, web browser and to keep security software up-to-date. This will reduce the probability of cybercriminals running bad programs onto your computer or mobile device. Kaspersky Lab would also like to remind users that hacked email accounts can allow attackers access to all the information stored in your mailbox including other logins and passwords. We recommend you to use strong passwords and two-factor authentication if possible."
According to Darya Gudkova, head of content analysis and research at Kaspersky Lab, ''Gadgets have become popular even among those who had little interaction with computers and are less familiar with computer security. This opens up new vectors of attacks for spammers and phishers. To protect themselves, users should remember not to open emails from unknown senders and especially not to click any links in these emails, which inevitably pose a risk to user security. Clicking unsafe links threatens user security regardless of which device is used – they pose a danger to desktop computers and mobile gadgets alike.''
 Where has the spam gone
Where has the spam gone
The list of countries most frequently targeted by malicious emails has undergone some changes since the third quarter of last year. The US's share (14%) grew 3.68 percentage points (pp) while the contribution of the UK (9.9%) and Germany (9.6%) decreased by 2.27 and 1.34 pp respectively. As a result, the US, which was third in the previous quarter, returned to the top of the rating in Q1 2014.
Sources of spam by country
The top three spam sources remained unchanged from the previous quarter:
- China (-0.34 percentage points), the US (+1.23 pp) and South Korea (-0.91 pp).
In Q1 2014, China was the leading spam with 21.93% (-0.34 pp) of all distributed spam. - It was followed by the United States, whose contribution was 18.81% (+1.23 percentage points) South Korea came third with 12.95% (-0.91 pp). Russia outstripped Taiwan and moved to fourth place, one position up from the previous quarter (+0.34 pp)
- Next came India at the sixth place (3.56%), Vietnam (3.18%), Ukraine (2.25%),Romania (1.92%) and the tenth place was Japan (1.92%)
Phishing
The email and search portals category topped the rating of the phishers' most popular targets (36.6 per cent of all attacks). Second came social networking sites with 26 per cent followed by financial and e-pay organizations and banks (14.7 per cent).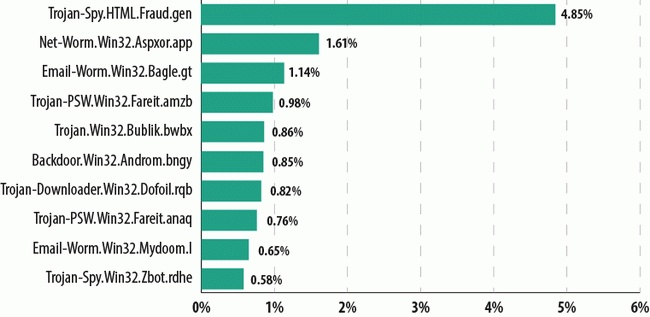
Malicious attachments in email
The main goal of most malicious programs distributed via email is to steal confidential data. However, in Q1 malware capable of spreading spam and launching DDoS attacks was also popular. Most popular malicious programs are now multifunctional - they can steal data from the victim computer, make the computer part of a botnet, or download and install other malicious programs without the user's knowledge.
- Trojan-Spy.HTML.Fraud.gen remained the most popular malicious program spread by email in the first quarter of the year. This malicious program is designed to look like an HTML page used as a registration form for online banking services. It is used by phishers to steal financial information.
- In second and seventh places came the Net-Worm.Win32.Aspxor worms. These net worms are designed to spread spam. They automatically infect sites, load and run other programs, and collect valuable information stored on the computer such as passwords and other data to access email and FTP accounts.
- Email-Worm.Win32.Bagle.gt, a long-time resident of the Top 10, came third. The main functionality of any worm is to harvest email addresses found on an infected computer. The Bagle worm can also accept remote commands to download malicious files from the Internet without the user's knowledge.
- Fourth and eighth places were occupied by Fareit family Trojans, which were most actively distributed in January. These programs were designed to steal user logins and passwords, launch DDoS attacks and download and run random software.


















